Startup Pricing Strategy
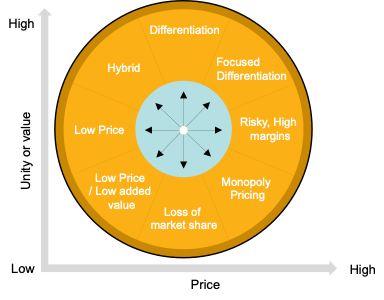
Ideas from Bowman’s strategy Clock
The Bowman's strategy clock is a model used in marketing to identify and analyse the competitive position of a company's product or service. It is named after Cliff Bowman, who developed the model in the 1980s.
The Bowman's strategy clock visually represents a company's pricing strategy and positioning in the market. The clock is divided into eight segments, each representing a different pricing strategy. The eight strategies are:
1. Low price: This strategy involves offering a product or service at a lower price than competitors to attract price-sensitive customers. This approach undercuts competitors by offering similar quality products at a lower price. Walmart, for example, embraces this strategy, focusing on everyday low prices as a primary selling point.
2. Differentiated: This strategy involves offering a unique product or service that is not easily comparable to competitors' offerings and charging a premium price for it. Businesses justify higher prices due to the distinctive value offered. Apple embodies this strategy, offering high-end, innovative technology that differentiates them from competitors.
3. Cost-plus pricing: This strategy involves setting the price of a product or service by adding a markup to the cost of production. This straightforward pricing approach is frequently used in retail, like in independent bookstores, where the retail price often is the wholesale cost plus a standard markup.
4. Penetration pricing: This strategy involves setting a low initial price for a product or service to quickly gain market share, with the intention of raising prices once the product or service has gained popularity. Businesses set a low initial price to lure customers, intending to raise the price later. Amazon used this strategy with Kindle, pricing it low initially to boost its adoption.
5. Economy pricing: This strategy involves offering a basic product or service at a low price to appeal to budget-conscious customers. An example of this would be budget airlines like Jetstar, which offer no-frills flight services at the lowest possible prices.
6. Price skimming: This strategy involves setting a high initial price for a product or service, then gradually lowering the price over time as competitors enter the market and demand for the product or service decreases. This strategy is common with new technology, such as the PlayStation console releases, starting high and then gradually lowering the price.
7. Premium pricing: This strategy involves setting a high price for a product or service to convey its quality, exclusivity, or luxury status. This often works for brands that offer high-quality products or services, like Rolex watches, projecting an image of luxury, exclusivity, and superior craftsmanship. Just charging high price in the pretence of high quality may not be sustainable as disillusionment from the promise may deteriorate brand value rapidly.
8. Psychological pricing: This strategy involves setting prices that have a psychological effect on customers, such as using odd numbers or prices that end in "9" to make the product or service seem more attractive. For example, 9.99 or 9.95 feels better than 10.00. It's a subtle perception game but proves quite effective.
The Bowman's strategy clock helps startups analyse their competitors' pricing strategies and identify potential opportunities to differentiate their products or services in the market. It also helps companies determine the optimal pricing strategy for their products or services to maximise profitability and gain a competitive advantage.
© Sameer Babbar
sbabbar@sameerbabbar.com
Disclaimer: This is for information only. It does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs. The author, his company his associates, his directors, his staff, his consultants, and his advisors do not accept liability for any loss or damage, including without limitation, any loss, which may arise directly or indirectly from the use of or reliance on the information provided.